3. Calculation of Line Loss
The calculation method for line loss is as follows:
(1) DC cable bears two currents
① Charging current (long-term)
The charging current varies over time, which is a variable. ***Generally speaking, the charging current is 0.1C of the rated capacity of a single battery, which means that the charging current of a 100Ah battery * “* is 100Ahx0.1C=10A. This value varies over time. When the float voltage value of this battery or group of batteries is reached, the charging current will become very small, to the milliampere level, so the charging current flowing through the cable does not account for line loss.
② Discharge current
The discharge current is a relatively constant quantity that is directly proportional to the load of the equipment (UPS or other inverter equipment). Generally speaking, if the load remains constant, the discharge current is a constant value. When it flows through a certain length of cable, it will generate a voltage drop (i.e. line loss).
(2) Definition of Line Loss
The voltage generated by a unit size of current flowing through a unit length of cable. It can also be considered that the so-called line loss refers to the voltage drop caused by the current flowing from the end of the battery to the input of the charger.
(3) Calculation method of line loss
According to Ohm’s law, line loss: U=IR
U: Line loss voltage
I: Discharge current of battery pack
R: Cable resistance value.
Discharge current:
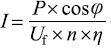
In the formula, P: rated power of UPS cos φ: load power factor
Uf: critical discharge voltage of the battery
n: Number of batteries
n: Efficiency of UPS inverter (0.88~0.95)
The resistance value of a cable is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. Is R=ρ? L/S (ρ: Conductivity of conductor).
(4) According to the above method and formula, taking a 400kVA UPS as an example, with a backup time of 1 hour, full load operation, and a DC cable length of 60m, the line loss is calculated.
Calculate according to the formula:
① The DC starting voltage of the MX series 400kV AUPS is 384V, with 32 units per group (the calculation method for the delay time and battery capacity of high-power UPS will not be discussed here). The load power factor is 0.9, and the inverter efficiency is taken as 0.92
Discharge current:

② Cross sectional area of battery cable
First, select the BVR240 cable with a wire diameter of 240mm2
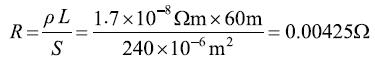
③ Line loss
U=IR=1164.59A×0.00425Ω=4.94V
④ Since the line loss cannot exceed 3V, selecting a 240mm2 cable is clearly not suitable.
⑤ So selecting two BVR240 cables in parallel, the calculated line loss is U=IR=1164.59A × 0.002125 Ω=2.47V. This specification of cable is suitable.
4. Conclusion
From the above, it can be concluded that for a 400kVA UPS, if its DC cable length is 60m, the cable cross-section to be selected is 480mm2, and its line loss is 2.47V, which meets the requirements. Another point to note here is that line loss is not related to the number of battery packs or the capacity of the battery pack. It is only related to the load capacity (discharge current) carried by the UPS and the DC starting voltage of the UPS itself (i.e. the number of single battery packs).


